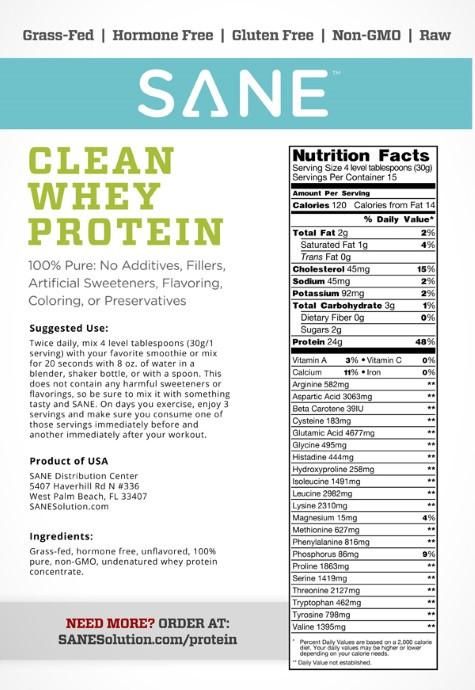
Clean Whey is made from raw milk. Flash pasteurization (163 F for 15 seconds) only happens one time at the very end of the manufacturing process, in accordance with FDA, USDA, and Wisconsin Department of Health regulations.
Because our WPC is only pasteurized for 15 seconds at 163 F it remains undenatured and tests very high in cystine and whey protein fractions, including immunoglobulin, lactoferrin and glycomacropeptides.
Additionally the FDA does not require whey to be heat pasteurized if proper filtration methods are used. From section 403 (h)(3) of the FFD&CA (page 84 – 85): http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Food/GuidanceRegulation/UCM291757.pdf
“a. If the product is whey, pasteurization is not required, provided:
(1) The product is acid whey (pH less than 4.7); or
(2) It is processed in RO or UF (ultra filtration) equipment at temperatures at or below 7C (45F).
b. If the product is raw milk for pasteurization, the product may be concentrated by the use of RO or UF membrane filtration without pasteurization, prior to the entrance into the equipment, provided the following sampling, testing, design, installation and operational criteria are met:
(1) Prior to processing, all raw milk supplies are sampled and tested for antibiotic residues in accordance with the provisions of Appendix N.;
(2) The RO or UF filtration system is designed and operated to assure that milk or milk product temperature is maintained at or below 18.3ºC (65ºF) throughout the process provided that the product temperature may rise above 18.3ºC (65ºF) for a period of not more than fifteen (15) minutes, further provided that should the product temperature rise above 21.1ºC (70ºF), the product shall be either immediately diverted to the system’s balance tank until the product is again below 18.3ºC (65ºF) or diverted to exit the system entirely. Diverted product that has exited the system shall be either discarded, immediately cooled to below 7°C (45°F), or immediately pasteurized;
(3) The RO or UF system must be equipped with temperature monitoring and recording devices that comply with the applicable specifications outlined in Appendix H. of this Ordinance. At a minimum, milk or milk product temperature shall be monitored and recorded prior to entering the system, prior to entering each stage of the modules in series that contains cooling, and the retentate stream prior to any final cooler and upon exiting the system;…”